New publications
Please find here under a list with recently published papers on the use of extraction chromatography that we'll update frequently.
We will also posts links to publications that might hopefully be of interest for you on our Bluesky account.
We hope that this will be of help for your work!
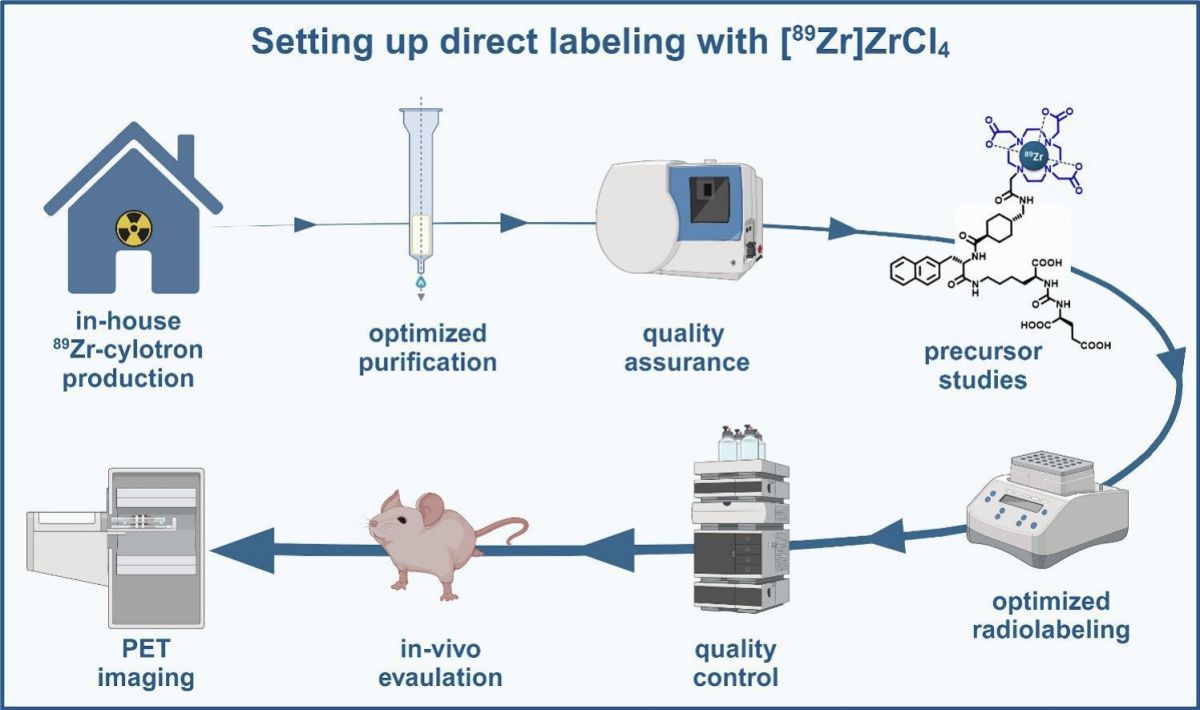
Serge K. Lyashchenko, Tuan Tran, Jason S. Lewis et al. "[89Zr]ZrCl4 for direct radiolabeling of DOTA-based precursors" Nuclear Medicine and Biology, Volumes 136–137, 2024, 108943.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2024.108943
Abstract:
Introduction
Zirconium-89 (89Zr) is a positron emitter with several advantages over other shorter-lived positron emission tomography (PET) compatible radiometals such as gallium-68 or copper-64. These include practically unlimited availability, extremely low cost, greatly facilitated distribution logistics, positron energy fit for medical PET imaging, and sufficiently long physical half-life to enable PET imaging at later time points for patient-specific dosimetry estimations. Despite these apparent benefits, the reception of 89Zr in the nuclear medicine community has been tepid. The driving factor for the absence of broader adaptation is mostly routed in its final formulation — [89Zr]zirconium oxalate. While serving as a suitable precursor solution for the gold standard chelator deferoxamine (DFO), [89Zr]Zr-oxalate is inaccessible for the most commonly used chelators, such as the macrocyclic DOTA, due to its pre-chelated state.
Consequently, pioneering work has been conducted by multiple research groups to create oxalate-free forms of [89Zr]Zr4+, either via chemical conversion of oxalate into other counterion forms or via direct radiochemical isolation of [89Zr]ZrCl4, showing that [89Zr]Zr-DOTA complexes are possible and stable. However, this success was accompanied by challenges, including complex and labor-intensive radiochemical processing and radiolabeling procedures as well as the relatively minuscule conversion rates. Here, we report on the direct production of [89Zr]ZrCl4 avoiding oxalate and metal contaminants to enable efficient radiolabeling of DOTA constructs.
Methods
We based our direct production of [89Zr]ZrCl4 on previously reported methods and further optimized its quality by including an additional iron-removing step using the TK400 Resin. Here, we avoided using oxalic acid and effectively minimized the content of trace metal contaminants. Our two-step purification procedure was automated, and we confirmed excellent radionuclide purity, minimal trace metals content, great reactivity over time, and high specific molar activity. In addition, DOTA-based PSMA-617 and DOTAGA-based PSMA-I&T were radiolabeled to demonstrate the feasibility of direct radiolabeling and to estimate the maximum apparent specific activities. Lastly, the biodistribution of [89Zr]Zr-PSMA-617 was assessed in mice bearing PC3-PIP xenografts, and the results were compared to the previously published data.
Results
A total of 18 batches, ranging from 6.9 to 20 GBq (186 to 541 mCi), were produced. The specific molar activity for [89Zr]ZrCl4 exceeded 0.96 GBq (26 mCi) per nanomole of zirconium. The radionuclidic purity was >99 %, and the trace metals content was in the
Conclusion
In this work, we report on a suitable application of TK400 Resin to remove iron during [89Zr]ZrCl4 radiochemical isolation. The breakthrough allows for direct radiolabeling of DOTA-based constructs with [89Zr]ZrCl4, leading to high apparent molar activities and excellent conversion rates.
TBP and TK400 Resins
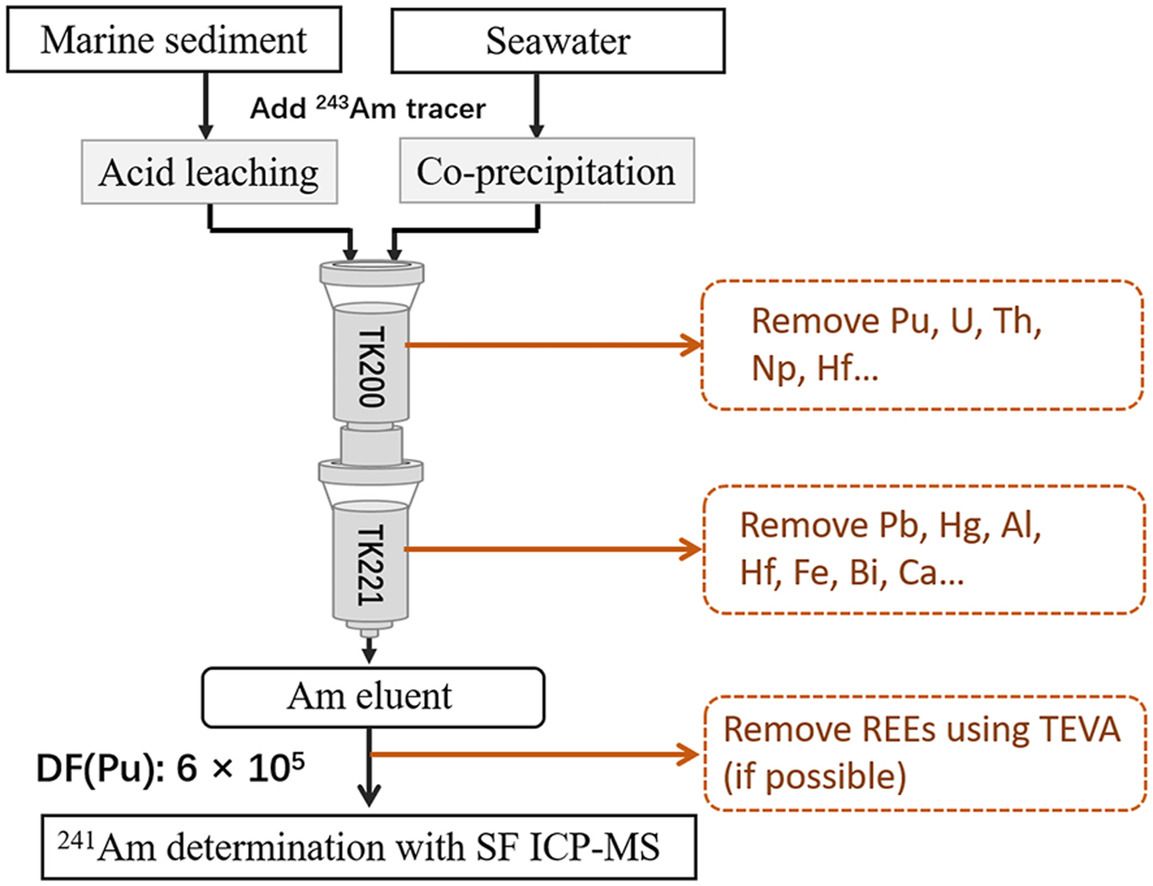
Ling Zhang & Emilia Vassileva. "Determination of ultra-trace level 241Am in marine sediment and seawater by combining TK200-TK221 tandem-column extraction chromatography and SF ICP-MS"
Talanta, 271, 2024, 25724, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2024.125724
Abstract:
Sound strategies for marine chemical monitoring call for measurement systems capable of producing comparable analytical results with demonstrated quality. This work presents the development and validation of a new analytical procedure for the determination of the 241Am mass fraction in marine sediment and seawater samples at low levels.
The procedure includes a tandem-column extraction chromatography for separation of 241Am and sector field-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SF ICP-MS) for its determination.
The separation is based on the application of two new extraction resins, TK200 and TK221. The acid leaching method was employed for the pre-treatment of marine sediments, while Fe(OH)3 co-precipitation was used for Am pre-concentration in seawater samples. The extraction behaviors of Am on TK221 resins in the different acidic mediums were investigated.
The removal capabilities of the tandem TK200-TK221 columns for the 241Am in the presence of interfering elements including Pu, Pb, Hg, Bi, Tl, Pt, Hf, U, and Th were carefully investigated and the corresponding decontamination factors (DFs) estimated to be in the range from 104 to 106. The main interfering element Pu was efficiently removed with a DF of about 6 × 105. Matrix rare earth elements (REEs) in marine sediments were further removed by the application of TEVA resins.
241Am mass fraction was quantified by the application of external calibration and SF ICP-MS.
Following the recommendations of the ISO/IEC 17025 guidelines, the validation of the analytical procedure was accomplished by executing it on the certified reference material (CRM) IAEA-385 (marine sediment) and the seawater IAEA-443 reference materials (RM). The obtained results showed that 241Am mass fractions were accurately determined in both reference samples, with excellent reproducibility (2.1 % and 7.6 %) and low LODs (0.4 fg g−1 and 0.2 fg g−1). The relative expanded uncertainties (k = 2) obtained were 17.1 % and 29.0 %, respectively. The overall analytical times for the application of the proposed procedure on the marine sediment and seawater samples were evaluated to be only about 9 h and 6.5 h, respectively. It shows great advantages for its potential applications for emergency monitoring of 241Am contamination in the marine environment.
TK221, TK200 and TEVA Resins
Tosato, M., Gandini, A., Happel, S. et al. Chromatographic separation of silver-111 from neutron-irradiated palladium target: toward direct labeling of radiotracers. EJNMMI radiopharm. chem. 8, 43 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41181-023-00232-0
Abstract:
Background
Silver-111 is a promising β−-emitting radioisotope with ideal characteristics for targeted radionuclide therapy and associated single photon emission tomography imaging. Its decay properties closely resemble the clinically established lutetium-177, making it an attractive candidate for therapeutic applications. In addition, the clinical value of silver-111 is further enhanced by the existence of the positron-emitting counterpart silver-103, thus imparting a truly theranostic potential to this element. A so-fitting matching pair could potentially overcome the current limitations associated with the forced use of chemically different isotopes as imaging surrogates of lutetium-177, leading to more accurate and efficient diagnosis and treatment. However, the use of silver-111-based radiopharmaceuticals in vivo has faced obstacles due to the challenges related to its production and radiochemical separation from the target material. To address these issues, this study aims to implement a chromatographic separation methodology for the purification of reactor-produced silver-111. The ultimate goal is to achieve a ready-to-use formulation for the direct radiolabeling of tumour-seeking biomolecules.
Results
A two-step sequence chromatographic process was validated for cold Ag-Pd separation and then translated to the radioactive counterpart. Silver-111 was produced via the 110Pd(n,γ)111Pd nuclear reaction on a natural palladium target and the subsequent β−-decay of palladium-111. Silver-111 was chemically separated from the metallic target via the implemented chromatographic process by using commercially available LN and TK200 resins. The effectiveness of the separations was assessed by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy and γ-spectrometry, respectively, and the Ag+ retrieval was afforded in pure water. Recovery of silver-111 was > 90% with a radionuclidic purity > 99% and a separation factor of around 4.21·10−4.
Conclusions
The developed separation method was suitable to obtain silver-111 with high molar activity in a ready-to-use water-based formulation that can be directly employed for the labeling of radiotracers. By successfully establishing a robust and efficient production and purification method for silver-111, this research paves the way for its wider application in targeted radionuclide therapy and precision imaging.
LN and TK200 Resin
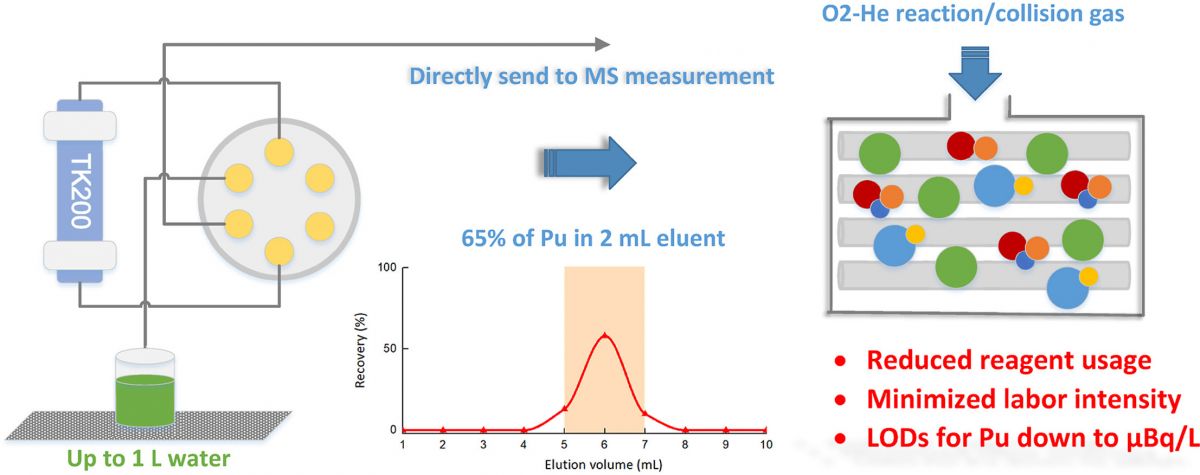
Youyi Ni, Wenting Bu, Ke Xiong, Sheng Hu, Chuting Yang, Liguo Cao. "A novel strategy for Pu determination in water samples by automated separation in combination with direct ICP-MS/MS measurement"
Talanta, Volume 262, 2023, 124710, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124710.
Abstract:
Methods for Pu determination in water samples has been longtime studied but they generally involved tedious manual operations. In this context, we proposed a novel strategy for accurate determination of ultra-trace Pu in water samples by the combination of fully automated separation with direct ICP-MS/MS measurement. A recently commercialized extraction resin TK200 was used for single-column separation due to its distinctive nature. Acidified waters up to 1 L were directly loaded to the resin at high flow rate (15 mL min−1) with omitting the frequently used co-precipitation process. Small volumes of dilute HNO3 were used for column washing, and Pu was efficiently eluted within only 2 mL 0.5 mol L−1 HCl-0.1 mol L−1 HF with a stable recovery (65%). This separation procedure was fully automated under the control of user program, meanwhile the final eluent was compatible for direct ICP-MS/MS measurement without extra sample treatment. In that way, both the labor intensity and reagent consumption were minimized compared with existing methods. With the high decontamination (104 to 105) of U in the chemical separation and the further elimination of uranium hydrides under oxygen reaction model during ICP-MS/MS measurement, the overall interference yields of UH+/U+ and UH2+/U+ were down to 10−15. The limits of detection (LODs) of this method reached 0.32 μBq L−1 for 239Pu and 2.00 μBq L−1 for 240Pu, which were much lower than those stipulated in the general guidelines for drinking water standards, suggesting this method was promising in routine or emergency radiation monitoring. Furthermore, the established method was successfully applied in a pilot study to determine global fallout derived Pu in surface glacier samples with extremely low concentrations of 239+240Pu, which suggested the method would also be feasible in glacial chronology studies in the future.
TK200 Resin
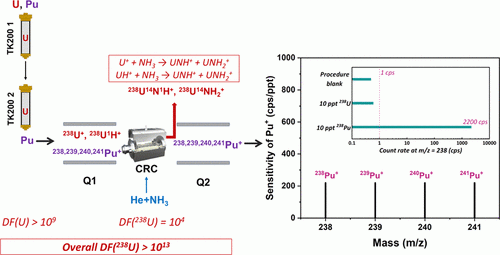
Zhao Huang, Xiaolin Hou and Xue Zhao: Rapid and Simultaneous Determination of 238Pu, 239Pu, 240Pu, and 241Pu in Samples with High-Level Uranium Using ICP-MS/MS and Extraction Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 34, 12931–12939. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02526
Abstract:
As the most important plutonium isotopes, 238Pu, 239Pu, 240Pu, and 241Pu are normally measured by two to three techniques, which are tedious, time-consuming, and not suitable for rapid analysis in emergency situations. Recently, ICP-MS has become a competitive technique for the rapid measurement of 239Pu, 240Pu, and 241Pu.
However, ICP-MS is difficult to measure 238Pu due to the serious isobaric interference of 238U. This work reports a rapid analytical method to solve this problem for the simultaneous determination of 238Pu, 239Pu, 240Pu, and 241Pu using triple-quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) combined with chemical separation. Chemical separation achieved a high decontamination factor of 2.12 × 109 for the most critical interfering element, uranium, by using two sequential TK200 columns.
The interferences of 238U1H+ and 238U+ were effectively eliminated by using 12 mL/min He–6 mL/min NH3 as the reaction gases in the octupole collision/reaction cell in ICP-MS/MS. Combined with chemical separation, the overall elimination efficiency of 238U1H+ reached 3.6 × 1017, which is 105 times better than the reported method.
With the high 238U+ elimination efficiency of 1.12 × 104 in the ICP-MS/MS measurement, the overall removal efficiency of 238U+ reached 1013, guaranteeing accurate determination of femtogram-level 238Pu as well as 239Pu, 240Pu, and 241Pu in the samples containing milligram-level 238U. The detection time is reduced to minutes, well fulfilling the requirement of rapid analysis. This method is validated by analyzing the standard reference material and the spiked samples.
TK200 Resin
Llopart-Babot, I., Vasile, M., Qiao, J. et al. "Optimization of the radiochemical separation and determination for 147Pm and 151Sm in nuclear waste samples"
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry (2024) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-024-09550-2
Abstract:
This work describes the development and optimization of the radiochemical separation of 147Pm and 151Sm. The two main challenges addressed were: the radiochemical separation of the lanthanides by using LN Resin and DGA,N Resin, and the quantification of the chemical recovery of 147Pm with a non-isotopic analogue (i.e. neodymium). The applicability of radiochemical separation procedures was investigated by using spiked samples. The optimized radiochemical separation procedure by using LN Resin was applied to a reactor cooling water primary coolant sample with an automated system. Sector Field Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (SF-ICP-MS) was used to determine the chemical recoveries.
DGA,N Resin, LN Resin
Brisudová, S., Rajec, P., Leporis, M. et al. Cyclotron production of 68Ga and "in house" preparation of positron emission tomography (PET) radiopharmaceuticals.
J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08732-0
Abstract:
Solid targets and a medical cyclotron were used for the large-scale preparation of 68Ga. The target preparation, proton irradiation of a 68Zn-enriched target, dissolution of the target, separation of 68Ga from zinc, and labelling procedure for the [68Ga]Ga-DOTATOC, [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC, and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 radiopharmaceutical are presented. The radiopharmaceuticals were prepared with a good manufacturing practices quality of up to 6 GBq of the final product per batch at the end of synthesis (EOS) time. A quality control of 68Ga-labelled tracers showed an acceptable radiochemical purity and stable product at least five hours after the EOS. A separation procedure for the effective separation of 68Ga from an iron interferent was developed.
TK400 Resin
I. Llopart-Babot, M. Vasile, A. Tarancón, H. Bagán, A. Dobney, S. Boden, M. Bruggeman, M. Leermakers, J. Qiao, P. Warwick : Investigation of a new approach for 36Cl determination in solid samples using plastic scintillators.
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2022, 110646, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110646
Abstract
This work reports a new approach for the determination of 36Cl in radioactive waste samples from nuclear decommissioning, wherein novel plastic scintillator (PS) materials were used for the concentration of 36Cl prior to the detection with scintillation counting.
Different plastic scintillator (PS) materials were tested for their selective absorption and detection of 36Cl activity in solid samples. PS microspheres (PSm), cross-linked PSm (CPSm) and PS resin have been investigated. PS resin was identified as the most suitable material for 36Cl analysis.
Pyrolysis and subsequent trapping of the volatile elements in a bubbler was used. The trapping solution was finally loaded onto a cartridge of the PS resin. Scintillation counting and ion chromatography were used to determine the activity concentration and the chemical recovery, respectively.
TK-TcScint
McNeil, S.W., Van de Voorde, M., Zhang, C. et al. A simple and automated method for 161Tb purification and ICP-MS analysis of 161Tb.
EJNMMI radiopharm. chem. 7, 31 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41181-022-00183-y
Abstract:
Background
161Tb is a radiolanthanide with the potential to replace 177Lu in targeted radionuclide therapy. 161Tb is produced via the neutron irradiation of [160Gd]Gd2O3 targets, and must be purified from 160Gd and the decay product 161Dy prior to use. Established purification methods require complex conditions or high-pressure ion chromatography (HPIC) which are inconvenient to introduce in a broad user community. This study aims to find a simpler small solid-phase extraction (SPE) column method for 161Tb purification that is more suitable for automation with commercially available systems like TRASIS.
Results
We first tested the distribution coefficients on TK211 and TK212 resins for the separation of Gd, Tb, and Dy, and subsequently developed a method to separate these metal ions, with an additional TK221 resin to concentrate the final product. A side-by-side comparison of the products purified using this new method with the HPIC method was undertaken, assessing the radionuclidic purity, chemical purity regarding Gd and Dy, and labeling efficiency with a standard chelate (DOTA) and a novel chelate (crown). The two methods have comparable radionuclidic purity and labeling efficiency. The small SPE column method reduced Gd content to nanogram level, although still higher than the HPIC method. An ICP-MS method to quantify 161Tb, 159Tb, 160Gd, and 161Dy was developed with the application of mass-shift by ammonia gas. Last, 161Tb produced from the small SPE column method was used to assess the biodistribution of [161Tb]Tb-crown-αMSH, and the results were comparable to the HPIC produced 161Tb.
Conclusions
161Tb was successfully purified by a semi-automated TRASIS system using a combination of TrisKem extraction resins. The resulting product performed well in radiolabelling and in vivo experiments. However, improvement can be made in the form of further reduction of 160Gd target material in the final product. An ICP-MS method to analyze the radioactive product was developed. Combined with gamma spectroscopy, this method allows the purity of 161Tb being assessed before the decay of the product, providing a useful tool for quality control.
TK212 and TK211
J. Svedjehed, M. Bas, S. Happel, K. Gagnon. Poster: P-80 - New extractant-impregnated iTLC-SG paper facilitates improved TLC analysis for Cu radiolabelled peptides.
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, Volumes 114–115, Supplement, November–December 2022, Page S72, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8051(22)02234-X
Upcoming CU Sheets
Papp, I., Vajda, N. & Happel, S.: "An improved rapid method for the determination of actinides in water"
J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08389-9
Abstract:
A new rapid method has been developed for the determination of Th, Pu, Np, U, Am and Cm isotopes in water samples of about 1 L. Actinides are pre-concentrated by co-precipitation with Ca phosphate, sequentially separated on stacked TEVA and TK221 cartridges and measured by alpha spectrometry. The TK221 extraction chromatographic resin contains i.e. CMPO and DGA extractants. It has been characterized by measuring the weight distribution ratios (Dw) of actinides which are higher than 1000 for all actinides in 3 M HNO3. The method has been optimized, applied for the analysis of tap and seawater samples and validated by participating in an IAEA proficiency test. Chemical recoveries for all actinides are better than 50%. The method can be performed within one day.
TK221 Resin & TEVA Resin
Llopart-Babot, I., Vasile, M., Dobney, A. et al. On the determination of 36Cl and 129I in solid materials from nuclear decommissioning activities.
J Radioanal Nucl Chem 331, 3313–3326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-022-08327-9
Abstract:
Determination of the 36Cl and 129I massic activities using pyrolysis combined with radiochemical separation (using a Cl-resin) in concrete and graphite samples from decommissioning waste originating from Belgian Reactor 3 and 1 (SCK CEN, Belgium), respectively, is described. Liquid scintillation counting is used for their quantification. The chemical recovery of the procedure was evaluated by determining the stable chlorine with ion chromatography and stable iodine with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The method was optimized and verified by spiking inactive solid materials.
CL Resin
Svedjehed, J., Pärnaste M., Gagnon K. "Demystifying solid targets: Simple and rapid distribution-scale production of [68Ga]GaCl3 and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11".
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, Volumes 104–105, 2022, Pages 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2021.10.002.
Abstract:
Background
As the demand for 68Ga continues to grow, there is increasing interest in single-to-multi-Curie production quantities of both [68Ga]GaCl3 and tracers such as [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11. While such quantities are possible with solid targets, this implementation is often challenging as it typically requires significant site expertise for solid target processing and careful operator-dependent synchronization of multiple independent time-sensitive chemistry steps. Herein we focus on a fully automated solid target production and purification process whereby we avoid the need for tongs/tele-pliers, and have simplified the chemistry by implementing a single sequence (i.e. “time-list”) to execute cassette-based dissolution, purification, and labeling.
Methods
Electroplated 68Zn was irradiated in a PETtrace prototype automated solid target system. Following irradiation, and using a single FASTlab time-list, the 68Zn was automatically dissolved with HCl/H2O2 and purified as [68Ga]GaCl3 using a combination of resins (ZR/TK400, A8, TK200: Triskem). For select experiments, [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 was also produced on the same cassette/single time-list (N = 4), or, by kit labeling (N = 1). Efforts focused towards on-cassette production of [68Ga]GaCl3 strived to maximize activity and quality, whereas efforts focused towards on-cassette production of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 aimed at limiting the entire production cycle to 1 h including the irradiation time (i.e. start-of-bombardment ➔ end-of-synthesis [EOS]).
Results
For the high activity triplicate [68Ga]GaCl3 productions (i.e. 80 μA, 102 min, 216 ± 10 mg), [68Ga]GaCl3 was purified (end-of-bombardment ➔ end-of-purification [EOP]) in ~28 min with activity yields of 181 ± 8 GBq at EOP and average radiochemical yields of 66 ± 5%. Average AMAs of 2.26 ± 0.16 TBq/μmol using DOTA (N = 3) and 12.00 TBq/μmol using HBED (PSMA-11) (N = 1) at EOP were measured. For the single kit test, (80 μA, 120 min, 263 mg 68Zn) for which 18 mg ascorbic acid was added to the buffer, 199 GBq of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 was successfully produced (thin layer chromatography-based radiochemical purity >99% at 6 h EOS). Finally, for efforts focused at expedient [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11, up to 42 GBq [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 with a radiochemical yield of 51.2% was produced in 63 min, including beamtime, using 220 mg of 68Zn as target material.
Conclusion
With the goal of simplifying solid target production and purification efforts, automated methods using single-use, cassette-based approaches for rapid, large-scale, single time-list production of [68Ga]GaCl3 and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 were developed. These methods were simple to execute and yielded high quality multi-Curie levels of both [68Ga]GaCl3 and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11.
ZR Resin, TK400 Resin, A8 Resin and TK200 Resin
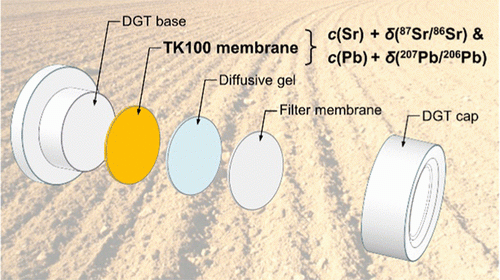
S. Wagner, J. Santner, J. Irrgeher: Selective Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films (DGT) for the Simultaneous Assessment of Labile Sr and Pb Concentrations and Isotope Ratios in Soils
Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 16, 6338–6346. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00546
Abstract:
A method using diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) for the accurate quantification of trace-level (μg L–1) Sr and Pb concentrations and isotope ratios [δSRM 987(87Sr/86Sr) and δSRM 981(207Pb/206Pb)] in labile, bioavailable element fractions in soils is reported.
The method is based on a novel poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE) membrane binding layer with combined di(2-ethyl-hexyl)phosphoric acid (HDEHP) and 4,4′(5′)-bis-t-butylcyclohexano-18-crown-6 (crown-ether) functionality with high selectivity for Sr and Pb (TK100 membrane). Laboratory evaluation of the TK100 DGT showed linear uptake of Sr over time (2–24 h) up to very high Sr mass loadings on TK100 membranes (288 μg cm–2) and effective performance in the range of pH (3.9–8.2), ionic strength (0.001–0.1 mol L–1), and cation competition (50–160 mg L–1 Ca in a synthetic soil solution matrix) of environmental interest.
Selective three-step elution of TK100 membranes using hydrochloric acid allowed us to obtain purified Sr and Pb fractions with adequate (≥75%) recovery and quantitative (≥96%) matrix reduction.
Neither DGT-based sampling itself nor selective elution or mass loading effects caused significant isotopic fractionation.
Application of TK100 DGT in natural soils and comparison with conventional approaches of bioavailability assessment demonstrated the method’s unique capability to obtain information on Sr and Pb resupply dynamics and isotopic variations with low combined uncertainty within a single sampling step.
Upcoming TK100 Discs
A. Hasson, Wen Jiang, N. Benabdallah et al.: Radiochemical Quality Control Methods for Radium-223 and Thorium-227 Radiotherapies
Cancer Biotherapy & Radiopharmaceuticals, Published Online:23 Sep 2022, https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2022.0023
Abstract
Background: The majority of radiopharmaceuticals for use in disease detection and targeted treatment undergo a single radioactive transition (decay) to reach a stable ground state. Complex emitters, which produce a series of daughter radionuclides, are emerging as novel radiopharmaceuticals. The need for validation of chemical and radiopurity with such agents using common quality control instrumentation is an area of active investigation. Here, we demonstrate novel methods to characterize 227Th and 223Ra.
Materials and Methods: A radio-TLC scanner and a gamma counter, two common and widely accessible technologies, as well as a solid-state alpha particle spectral imaging camera were evaluated for their ability to characterize and distinguish 227Th and 223Ra. We verified these results through purity evaluation of a novel 227Th-labeled protein construct.
Results: The gamma counter and alpha camera distinguished 227Th from 223Ra, enabling rapid and quantitative determination of radionuclidic purity. The radio-TLC showed limited ability to describe purity, although use under alpha particle-specific settings enhanced resolution. All three methods were able to distinguish a pure from impure 227Th-labeled protein.
Conclusions: The presented quality control evaluation for 227Th and 223Ra on three different instruments can be applied to both research and clinical settings as new alpha particle therapies are developed.
DGA Sheets
Ni Yuan, Quan An, Shan Xing, Xiongxin Dai, Xiaolin Hou, Yonggang Yang, Yan Ma. "Rapid determination of 99Tc in water samples using Ti(OH)3-TcO2 co-precipitation and TK200 resin by liquid scintillation counting"
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, Volumes 251–252, 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2022.106954
Abstract:
A novel method for the determination of 99Tc in water samples was developed using stable Re as a chemical yield tracer and TiCl3 as a reducing agent. The influences of several experimental parameters, including TiCl3 concentration, HCl concentration and reaction time, on the reduction of TcO4− and ReO4− as well as Ti(OH)3-TcO2-ReO2 co-precipitation were investigated. Tc(VII) and Re(VII) retained on TK200 resin were effectively eluted by 5 mL of 1 mol/L NH4SCN, which can be directly mixed with the scintillation cocktail for liquid scintillation counting. The results show that the chemical behaviors of Tc and Re are very consistent in the whole procedure. The decontamination factors of potential interferences from β-emitting nuclides mainly released from nuclear fuel reprocessing plants were also evaluated, and the minimum detectable activity concentration was calculated to be 0.08 Bq/L for 99Tc in water samples with a counting time of 2 h.
TK200 Resin
Kawabata, M., Motoishi, S., Ohta, A. et al.: "Large scale production of 64Cu and 67Cu via the 64Zn(n, p)64Cu and 68Zn(n, np/d)67Cu reactions using accelerator neutrons".
J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330, 913–922 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07987-3
Abstract:
Both 64Cu and 67Cu are promising radionuclides in nuclear medicine. Production yields of these radionuclides were quantified by irradiating 55.4 g of natural zinc with accelerator neutrons. Clinically suitable 64Cu and 67Cu yields were estimated by experimental based numerical simulations using 100 g of enriched 64Zn and 68Zn, respectively, and elevated neutron fluxes from 40 MeV, 2 mA deuterons. A combined thermal- and resin-separation method was developed to isolate 64Cu and 67Cu from zinc, resulting in 73% separation efficiency and 97% zinc recovery. Such methods can provide large scale production of 64Cu and 67Cu for clinical applications.
CU Resin and TK201 Resin
MCarmen Garcia Poyo et al.: "Laser ablation of microdroplets for copper isotopic analysis via MC-ICP-MS. Analysis of serum microsamples for the diagnosis and follow-up treatment of Wilson's disease."
J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2021, Accepted Manuscript, https://doi.org/10.1039/D0JA00494D
Abstract:
Cu isotopic analysis -can provide valuable hindsight when investigating Wilson’s disease (WD), but one of the problems related with this type of study is that usually low sample volumes are available and/or low Cu concentrations are found in these samples. This paper presents a new approach for Cu isotope ratio determination that requires only 1 µL of pre-treated serum sample per replicate (after Cu separation and preconcentration to a Cu concentration range between 0.3 and 4 mg L-1). Cu determination was carried out by direct µ-injection of 1µL of pretreated serum samples into an ICP-MS, offering a LOD of 3 µg L-1. For Cu isotopic analysis, the method presented is based on micro-volume deposition on a pure silicon wafer and subsequent ablation analysis by fs-LA-MC-ICP-MS. Cu isotopic analysis of NIST 3114 at 1 mg L-1 Cu concentration with the self-bracketing method provided average δ65Cu values of -0.01 ± 0.19‰ (2SD) and for internal precision values of 517 ppm. This method was deployed for analysis of serum samples from WD patients under different treatments, as well as healthy newborns and patients with other liver disorders. The results seem to link decreased δ65Cu values to Cu release from the liver, further demonstrating the interest of this type of analysis in the biomedical context.
CU Resin
Molecules 2021, 26(21), 6371; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216371
Abstract:
Today, 44Sc is an attractive radionuclide for molecular imaging with PET. In this work, we evaluated a 44Ti/44Sc radionuclide generator based on TEVA resin as a source of 44Sc. The generator prototype (5 MBq) exhibits high 44Ti retention and stable yield of 44Sc (91 ± 6 %) in 1 mL of eluate (20 bed volumes, eluent—0.1 M oxalic acid/0.2 M HCl) during one year of monitoring (more than 120 elutions). The breakthrough of 44Ti did not exceed 1.5 × 10−5% (average value was 6.5 × 10−6%). Post-processing of the eluate for further use in radiopharmaceutical synthesis was proposed. The post-processing procedure using a combination of Presep® PolyChelate and TK221 resins made it possible to obtain 44Sc-radioconjugates with high labeling yield (≥95%) while using small precursor amounts (5 nmol). The proposed method takes no more than 15 min and provides ≥90% yield relative to the 44Sc activity eluted from the generator. The labeling efficiency was demonstrated on the example of [44Sc]Sc-PSMA-617 and [44Sc]Sc-PSMA-I&T synthesis. Some superiority of PSMA-I&T over PSMA-617 in terms of 44Sc labeling efficiency was demonstrated (likely due to presence of DOTAGA chelator in the precursor structure). It was also shown that microwave heating of the reaction mixture considerably shortened the reaction time and improved radiolabeling yield and reproducibility of [44Sc]Sc-PSMA-617 and [44Sc]Sc-PSMA-I&T synthesis.
TEVA Resin and TK221 Resin
Thisgaard, H., Kumlin, J., Langkjær, N. et al. Multi-curie production of gallium-68 on a biomedical cyclotron and automated radiolabelling of PSMA-11 and DOTATATE. EJNMMI radiopharm. chem. 6, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41181-020-00114-9
Abstract
Background
With increasing clinical demand for gallium-68, commercial germanium-68/gallium-68 ([68Ge]Ge/[68Ga]Ga) generators are incapable of supplying sufficient amounts of the short-lived daughter isotope. In this study, we demonstrate a high-yield, automated method for producing multi-Curie levels of [68Ga]GaCl3 from solid zinc-68 targets and subsequent labelling to produce clinical-grade [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 and [68Ga]Ga-DOTATATE.
Results
Enriched zinc-68 targets were irradiated at up to 80 µA with 13 MeV protons for 120 min; repeatedly producing up to 194 GBq (5.24 Ci) of purified gallium-68 in the form of [68Ga]GaCl3 at the end of purification (EOP) from an expected > 370 GBq (> 10 Ci) at end of bombardment. A fully automated dissolution/separation process was completed in 35 min. Isolated product was analysed according to the Ph. Eur. monograph for accelerator produced [68Ga]GaCl3 and found to comply with all specifications. In every instance, the radiochemical purity exceeded 99.9% and importantly, the radionuclidic purity was sufficient to allow for a shelf-life of up to 7 h based on this metric alone. Fully automated production of up to 72.2 GBq [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 was performed, providing a product with high radiochemical purity (> 98.2%) and very high apparent molar activities of up to 722 MBq/nmol. Further, manual radiolabelling of up to 3.2 GBq DOTATATE was performed in high yields (> 95%) and with apparent molar activities (9–25 MBq/nmol) sufficient for clinical use.
Conclusions
We have developed a high-yielding, automated method for the production of very high amounts of [68Ga]GaCl3, sufficient to supply proximal radiopharmacies. The reported method led to record-high purified gallium-68 activities (194 GBq at end of purification) and subsequent labelling of PSMA-11 and DOTATATE. The process was highly automated from irradiation through to formulation of the product, and as such comprised a high level of radiation protection. The quality control results obtained for both [68Ga]GaCl3 for radiolabelling and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 are promising for clinical use.
Keywords: Gallium-68, Cyclotron, Accelerator, DOTATATE, PSMA-11, Solid target, Targetry
ZR Resin, LN Resin and TK200 Resin
Rodnick, M.E., Sollert, C., Stark, D. et al. Cyclotron-based production of 68Ga, [68Ga]GaCl3, and [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 from a liquid target. EJNMMI radiopharm. chem. 5, 25 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1186/s41181-020-00106-9
Abstract
Purpose:
To optimize the direct production of 68Ga on a cyclotron, via the 68Zn(p, n)68Ga reaction using a liquid cyclotron target. We Investigated the yield of cyclotron-produced 68Ga, extraction of [68Ga]GaCl3 and subsequent [68Ga]Ga-PSMA11 labeling using an automated synthesis module.
Methods:
Irradiations of a 1.0 M solution of [68Zn]Zn(NO3)2 in dilute (0.2–0.3 M) HNO3 were conducted using GE PETtrace cyclotrons and GE 68Ga liquid targets. The proton beam energy was degraded to a nominal 14.3 MeV to minimize the co-production of 67 Ga through the 68Zn(p,2n)67Ga reaction without unduly compromising 68Ga yields. We also evaluated the effects of varying beam times (50–75 min) and beam currents (27–40 μA). Crude 68Ga production was measured. The extraction of [68Ga]GaCl3 was performed using a 2 column solid phase method on the GE FASTlab Developer platform. Extracted [68Ga]GaCl3 was used to label [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 that was intended for clinical use.
Results:
The decay corrected yield of 68Ga at EOB was typically > 3.7 GBq (100 mCi) for a 60 min beam, with irradiations of [68Zn]Zn(NO3)2 at 0.3 M HNO3. Target/chemistry performance was more consistent when compared with 0.2 M HNO3. Radionuclidic purity of 68Ga was typically > 99.8% at EOB and met the requirements specified in the European Pharmacopoeia (< 2% combined 66/67Ga) for a practical clinical product shelflife. The activity yield of [68Ga]GaCl3 was typically > 50% (~ 1.85 GBq, 50 mCi); yields improved as processes were optimized. Labeling yields for [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 were near quantitative (~ 1.67 GBq, 45 mCi) at EOS. Cyclotron produced [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 underwent full quality control, stability and sterility testing, and was implemented for human use at the University of Michigan as an Investigational New Drug through the US FDA and also at the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital (RPA).
Conclusion:
Direct cyclotron irradiation of a liquid target provides clinically relevant quantities of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 and is a viable alternative to traditional 68Ge/68Ga generators.
Keywords: Gallium-68, Cyclotron targetry, Positron emission tomography, PSMA
ZR Resin and TK200 Resin
Svedjehed, J., Kutyreff, C.J., Engle, J.W. et al. Automated, cassette-based isolation and formulation of high-purity [61Cu]CuCl2 from solid Ni targets.
EJNMMI radiopharm. chem. 5, 21 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1186/s41181-020-00108-7
Abstract
Background:
A need for improved, cassette-based automation of 61Cu separation from irradiated Ni targets was identified given the growing interest in theranostics, and generally lengthy separation chemistries for 64Cu/64Ni, upon which 61Cu chemistry is often based.
Methods:
A method for separating 61Cu from irradiated natNi targets was therefore developed, with provision for target recycling. Following deuteron irradiation, electroplated natNi targets were remotely transferred from the cyclotron and dissolved in acid. The dissolved target solution was then transferred to an automated FASTlab chemistry module, where sequential TBP and TK201 (Triskem) resins isolated the [61Cu]CuCl2, removed Ni, Co, and Fe, and concentrated the product into a formulation suitable for anticipated radiolabelling reactions.
Results:
61Cu saturation yields of 190 ± 33 MBq/μA from energetically thick natNi targets were measured. The average, decay-corrected, activity-based dissolution efficiency was 97.5 ± 1.4% with an average radiochemical yield of 90.4 ± 3.2% (N = 5). The isolated activity was collected approximately 65 min post end of bombardment in ~ 2 mL of 0.06 M HCl (HCl concentration was verified by titration). Quality control of the isolated [61Cu]CuCl2 (N = 5) measured 58Co content of (8.3 ± 0.6) × 10− 5% vs. 61 Cu by activity, Ni separation factors ≥ (2.2 ± 1.8) × 106, EoB molar activities 85 ± 23 GBq/μmol and NOTA-based EoB apparent molar activities of 31 ± 8 MBq/nmol and 201 MBq/nmol for the 30 min and 3.3 h (N = 1) irradiations, respectively.
Conclusion:
High purity 61Cu was produced with the developed automated method using a single-use, cassette-based approach. It was also applicable for 64Cu, as demonstrated with a single proof-of-concept 64Ni target production run.
Keywords: 61Cu (radiocopper), Automation/automated, PET, Solid target, Dissolution, Recycling
TK201 Resin and TBP Resin
ZhongtangWang, ZhaoyaHuang, YunXie, ZhaoyiTan: "Method for determination of Pu isotopes in soil and sediment samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after simple chemical separation using TK200 resin"
Analytica Chimica Acta, Available online 29 August 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.063
Highlights
- For the first time, TK200 resin is applied in the determination of Pu isotopes in environmental sample.
- The developed chromatographic separation procedure using TK200 resin only takes 1.5 h.
- The obtained decontamination factor of U (>7.5 ×107) of this method is the highest reported value.
- The chemical recovery of Pu of this method is stably high (81-91%).
Abstract
Plutonium has been extensively studied in the environment, for the purpose of radiological assessment, environmental behavior study and nuclear emergency response. To determine Pu isotopes in environmental soil and sediment, a novel analytical method was established in this study using a new type of extraction resin, TK200 resin. Firstly an investigation was performed to study the extraction behaviors of Pu, U, Th, Hg, Tl, Pb, Bi and Hf on TK200 resin. On the basis of the results, a new chromatographic procedure was then proposed to separate Pu from the elements that interfere the accurate determination of Pu isotopes by mass spectrometry. Owing to the excellent separation efficiency between Pu and interfering elements (IEs) of the developed procedure, high decontamination factors (DFs) were obtained for IEs, e.g. the DF(U) (>7.5×107) was the highest reported value. The separation procedure was finally combined with HNO3 leaching, CaF2/LaF3 coprecipitation and sector field-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SF-ICPMS) measurement to establish a complete method. The established method was evaluated by analyzing four standard reference materials (soil, sediment), and the results showed that both 239+240Pu activity and 240Pu/239Pu isotopic ratio were accurately determined, with stable and high Pu chemical recoveries (81-91%). The whole analytical method only took about 15 h, and the limits of detection were calculated to be 0.13 - 0.24 fg g-1 for Pu isotopes (for 2 g soil or sediment), guaranteeing the rapid determination of ultra-trace level Pu in soil and sediment samples.
TK200
Esparza, D. et al.: "Fast-response flow-based method for evaluating 131I from biological and hospital waste samples exploiting liquid scintillation detection",
Talanta, 206, 2020, 120224, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120224
Abstract
Highlights
- I-131 is fastly determined in biological and hospital waste samples.
- A flow system allows the automatic and safe analysis of radioactive samples.
- Sample clean-up is achieved exploiting a really green-chemistry and fast-response method.
Abstract
This paper presents a fast and automatic flow-based method to extract 131I from biological samples and hospital waste, previous to liquid scintillation detection. 131I is a radionuclide extensively used in Nuclear Medicine due to their beta and gamma disintegrations, whereby hospitals have to manage the associated waste generation. The automatic developed system is based on Lab-On-Valve (LOV) flow-technique exploiting Cl-resin (135 mg per extraction). This methodology allows performing sample extractions and measurements on the same day, since the extraction frequency takes 1.4–4 h−1, depending on the analysed sample volume, plus up to 2 h of measurement for each vial. 131I is retained as iodine ion and eluted with sodium sulphide 0.2 mol L−1. The maximum sample volume that can be preconcentrated is 20 mL, reaching an extraction efficiency of 85 ± 5%. The minimum detectable activity (MDA) is 0.05 Bq, showing a precision of 7% RSD (n = 5). Both, biological samples (urine and saliva) and hospital waste samples can be satisfactorily analysed by the proposed system, obtaining recoveries between 90 and 110%. The developed method is then suitable to implement in hospitals, improving the surveillance of the 131I environmental release.
Keywords
131I, Flow analysis, Biological sample, Hospital waste, Cl-resin, Liquid scintillation counting
CL Resin
Tieu W. et al. "Rapid and automated production of Ga-68 chloride and Ga-68-DOTA-TATE on a medical cyclotron".
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, online 12 July 2019, In Press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2019.07.005
Abstract:
Introduction
The demand for Gallium-68 (68Ga) for labelling PET radiopharmaceuticals has increased over the past few years. 68Ga is obtained through the decayed parent radionuclide 68Ge using commercial 68Ge/68Ga generators. The principal limitation of commercial 68Ge/68Ga generators is that only a limited and finite quantity of 68Ga (
Methods
Enriched ZnCl2 was electrodeposited on a platinum backing using an NH4Cl (pH 2–4) buffer. The Zn target was irradiated with GE PETtrace 880 at 35 uA and 14.5 and 12.0 MeV beam energy. The irradiated Zn target was purified using octanol resin on an automated system.
Results
Following the described procedure, 68Ga was obtained in 6.30 ± 0.42 GBq after 8.5 min bombardment and with low radionuclidic impurities (66Ga (<0.005%) and 67Ga (<0.09%)). Purification on a single octanol resin gave 82% recovery with resulting [68Ga]GaCl3 obtained in 3.5 mL of 0.2 M HCl. [68Ga]GaCl3 production from irradiation to final product was 70%.
Conclusions
A straightforward procedure for producing 68Ga on a low energy medical cyclotron was described. Current efforts are focus on high activity production and radiolabelling using solid target produced 68Ga.
Keywords
Cyclotron, Ga-68, Solid targetry, PET, DOTA-TATE
TK400 Resin
Miller et al. "Antibiotic treatment affects the expression levels of copper transporters and the isotopic composition of copper in the colon of mice"
Abstract:
Copper is a critical enzyme cofactor in the body but also a potent cellular toxin when intracellularly unbound. Thus, there is a delicate balance of intracellular copper, maintained by a series of complex interactions between the metal and specific copper transport and binding proteins.
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is the primary site of copper entry into the body and there has been considerable progress in understanding the intricacies of copper metabolism in this region. The GI tract is also host to diverse bacterial populations, and their role in copper metabolism is not well understood.
In this study, we compared the isotopic fractionation of copper in the GI tract of mice with intestinal microbiota significantly depleted by antibiotic treatment to that in mice not receiving such treatment. We demonstrated variability in copper isotopic composition along the length of the gut. A significant difference, ∼1.0‰, in copper isotope abundances was measured in the proximal colon of antibiotic-treated mice. The changes in copper isotopic composition in the colon are accompanied by changes in copper transporters. Both CTR1, a copper importer, and ATP7A, a copper transporter across membranes, were significantly down-regulated in the colon of antibiotic-treated mice.
This study demonstrated that isotope abundance measurements of metals can be used as an indicator of changes in metabolic processes in vivo. These measurements revealed a host–microbial interaction in the GI tract involved in the regulation of copper transport.
CU Resin
Larenko et al. "Preparation of Zirconium-89 Solutions for Radiopharmaceutical Purposes: Interrelation Between Formulation, Radiochemical Purity, Stability and Biodistribution"
Molecules 2019, 24(8), 1534, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081534
Abstract:
Zirconium-89 is a promising radionuclide for nuclear medicine. The aim of the present work was to find a suitable method for obtaining zirconium-89 solutions for radiopharmaceutical purposes.
For this purpose, the ion exchange behavior of zirconium-89 solutions was studied. Radio-TLC (thin layer chromatography) and biodistribution studies were carried out to understand speciation of zirconium-89 complexes and their role in the development of new radiopharmaceuticals. Three methods of zirconium-89 isolation were studied using ZR (hydroxamate) and Chelex-100 resins. It was found that ZR-resin alone is not enough to obtain stable zirconium-89 formulations. An easy and effective method of reconstitution of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate to [89Zr]Zr-citrate using Chelex-100 resin was developed.
Developed procedures allow obtaining [89Zr]Zr-oxalate (in 0.1 M sodium oxalate solution) and [89Zr]Zr-citrate (in 0.1–1.0 M sodium citrate solution). These solutions are perfectly suitable and convenient for radiopharmaceutical purposes. Our results prove [89Zr]Zr-citrate to be advantageous over [89Zr]Zr-oxalate. During evaluation of speciation of zirconium-89 complexes, a new TLC method was developed, since it was proved that there is no comprehensive method
for analysis or zirconium-89 preparations. The new method provides valuable insights about the content of “active” ionic form of zirconium-89. The interrelation of the chromatographic behavior of zirconium-89 preparations and their biodistribution was studied.
ZR Resin
Riga et al. "Production of Ga-68 with a General Electric PETtrace cyclotron by liquid target"
Physica Medica Available online 25 October 2018 In Press, Corrected Proof,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2018.10.018
Abstract:
Purpose
In recent years the use of 68Ga (t1/2 = 67.84 min, β+: 88.88%) for the labelling of different PET radiopharmaceuticals has significantly increased. This work aims to evaluate the feasibility of the production of 68Ga via the 68Zn(p,n)68Ga reaction by proton irradiation of an enriched zinc solution, using a biomedical cyclotron, in order to satisfy its increasing demand.
Methods
Irradiations of 1.7 M solution of 68Zn(NO3)2 in 0.2 N HNO3 were conducted with a GE PETtrace cyclotron using a slightly modified version of the liquid target used for the production of fluorine-18. The proton beam energy was degraded to 12 MeV, in order to minimize the production of 67Ga through the 68Zn(p,2n)67Ga reaction. The product’s activity was measured using a calibrated activity meter and a High Purity Germanium gamma-ray detector.
Results
The saturation yield of 68Ga amounts to (330 ± 20) MBq/µA, corresponding to a produced activity of 68Ga at the EOB of (4.3 ± 0.3) GBq in a typical production run at 46 µA for 32 min. The radionuclidic purity of the 68Ga in the final product, after the separation, is within the limits of the European Pharmacopoeia (>99.9%) up to 3 h after the EOB. Radiochemical separation up to a yield not lower than 75% was obtained using an automated purification module. The enriched material recovery efficiency resulted higher than 80–90%.
Conclusions
In summary, this approach provides clinically relevant amounts of 68Ga by cyclotron irradiation of a liquid target, as a competitive alternative to the current production through the 68Ge/68Ga generators.
ZR Resin and TK200 Resin
Yu Tang et al.: "A Radiopharmaceutical [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab for ImmunoPET with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression In Vivo", Nuclear Medicine and Biology, Available online 8 February 2019, In Press, Accepted Manuscript,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2019.01.007
Abstract:
Introduction: The potential of the positron-emitting zirconium-89 (89Zr) (t1/2=78.4 h) has been recently reported for immune positron emission tomography (immunoPET) radioimmunoconjugates design. In our work, we explored the optimized preparation of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab, and evaluated 89Zr-labeled monoclonal antibody (mAb) construct for targeted imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) overexpressed in glioma. Methods: To optimize the radiolabeling efficiency of 89Zr with DFO-nimotuzumab, multiple immunoconjugates and radiolabeling were performed. Radiolabeling yield, radiochemical purity, stability, and activity assay were investigated to characterize [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab for chemical and biological integrity. The in vivo behavior of this tracer was studied in mice bearing subcutaneous U87MG (EGFR-positive) tumors received a 3.5±0.2 MBq/dose using PET/CT imaging. One group mice bearing subcutaneous U87MG (EGFR-positive) tumors received [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab (3.5±0.2 MBq, ~3 μg) (nonblocking) for immunoPET; the other group had 30 μg predose (blocking) of cold nimotuzumab 24 h prior to [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab.
Results: [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab was prepared with high radiochemical yield (>90%), radiochemical purity (>99%), and specific activity (115±0.8 MBq/mg). In vitro validation showed that [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab had an initial immunoreactive fraction of 0.99±0.05 and remained active for up to 5 days. A biodistribution study revealed excellent stability of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab in vivo compared with 89Zr as a bone seeker. High uptake in the liver and heart and modest penetration in the brain were observed, with no significant accumulation of activity in other organs. ImmunoPET studies also indicated prominent image contrast that remarkably high uptake up to ~20 %ID/g for nonblocking and ~2 %ID/g for blocking in tumor between 12-120 h after administration.
Conclusion: These studies developed a radiopharmaceutical [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab with optimized synthesis. The potential utility of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab in assessing EGFR status in glioma was demonstrated in
this study.
ZR Resin
Pin, C. and Gannoun, A.: "A triple tandem columns extraction chromatography method for isolation of highly purified Neodymium prior to 143Nd/144Nd and 142Nd/144Nd isotope ratios determinations" J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2018, Accepted Manuscript, https://doi.org/10.1039/C8JA00360B
Abstract:
A new separation scheme is presented for the isolation of Nd fractions highly purified from adjacent lanthanides, especially Ce and Pr, in preparation to demanding isotope ratios applications, e.g. determination of 142Nd/144Nd, or measurement of 143Nd/144Nd on very small samples by using NdO+ ion beams. Following sample dissolution with hydrofluoric and nitric acids, the method avoids lengthy evaporations, and does not require an oxidation stage to get rid of most of Ce as Ce(IV). The scheme is based on the concatenation of several small extraction chromatographic (EXC) columns filled with three different, commercially available resins, and used in successive tandem configurations, without intervening evaporation step. In the first column, filled with 0.25 ml of the well established TRU-resin, the LREE are separated from matrix elements, and directly stripped onto a second 1 ml column filled with an HEH[HEP]-based EXC material (LN2-resin), which performs an early separation of Nd from most of Ce and Pr, and from all Sm and heavier lanthanides. The Nd fraction separated in this way is eluted on-line onto a third column filled with 1 ml of resin based on a diglycolamide extracting agent (DGA-resin), for further removal of Ce and Pr impurities. Finally, the Nd fraction is stripped from the DGA column onto the previously used LN2 column for a second pass achieving an additional “skimming” of residual Ce and Pr. The LN2-DGA tandem column cycle can be repeated as many times as desired, thereby providing Nd in an extremely pure form.
TRU Resin, LN2 Resin and DGA Resin
Malinconico, M., Asp, J., Lang, C., Boschi, F., Tieu, W., Kuan, K., Guidi, G., Takhar, P.:"68Ga and 45Ti production on a GE PETtrace cyclotron using the ALCEO solid target"
J Nucl Med May 1, 2018 vol. 59 no. supplement 1 664 , presentation available online.
Abstract:
Objectives: The ALCEO solid target system has been developed by Comecer for cyclotron production of 64Cu 89Zr, 123I and 124I. ALCEO Solid Target is composed by one irradiation unit (PTS), one dissolution/transfer unit (EDS/FDS) and one purification module (TADDEO PRF); all the units work automatically, avoiding any radiation exposures to operators. Many sites are already producing these radioisotopes with yields respectively of >2mCi/µAh (64Cu), >0.4mCi/µAh (89Zr and 123I), >0.1mCi/µAh (124I). The aim of this work was to expand the use of the ALCEO system to also produce 68Ga and 45Ti. Production and labelling results will be presented as well. Methods 68Zn was electroplated onto a target shuttle and irradiated (with a typical current from 10µA to 30µA) with 12.1 MeV protons to produce 68Ga. Irradiated target was dissolved in 10M HCl. The 68Ga was separated from the irradiated 68Zn using LN resin (TRISKEM), then labelled to PSMA and DOTATATE using an Eckert and Ziegler Modular-Lab eazy synthesis module. Natural scandium was irradiated with 12.1 MeV protons, with a typical current of 10µA to produce 45Ti. Irradiated target was dissolved by drop-by-drop 6M HCl. The 45Ti was separated from the irradiated scandium using ZR resin (TRISKEM), then labelled manually to DFO mesylate salt . Results 68Ga is produced with a saturation yield of 1330±590 MBq/µA (N=2), and was successfully labelled to PSMA and DOTATATE with 79.2% and 76.0% synthesis yields and 99.0% and 91.3% radiochemical purity respectively. 45Ti is produced with a saturation yield of 312 MBq/µA (N=1). It was not successfully labelled to PSMA and DOTATATE, however the labelling efficiency for DFO mesylate salt was 41%. Conclusions The Comecer ALCEO solid target system has been used successfully to produce 64Cu, 89Zr, 68Ga and 45Ti. The produced PET-isotopes have a very high radio-purity and chemical-purity and they can be used for radio-labeling processes. Future work includes optimisation of separation processes, and production of 203Pb and 44Sc.
ZR Resin and LN Resin
Pupillo G. et al. :"New production cross sections for the theranostic radionuclide 67Cu"
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 415, 2018, 41-47, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2017.10.022
Abstract:
The cross sections of the 68Zn(p,2p)67Cu, 68Zn(p,2n)67Ga and 68Zn(p,3n)66Ga reactions were measured at the ARRONAX facility by using the 70 MeV cyclotron, with particular attention to the production of the theranostic radionuclide 67Cu. Enriched 68Zn material was electroplated on silver backing and exposed to a low-intensity proton beam by using the stacked-foils target method. Since 67Cu and 67Ga radionuclides have similar half-lives and same γ-lines (they both decay to 67Zn), a radiochemical process aimed at Cu/Ga separation was mandatory to avoid interferences in γ-spectrometry measurements. A simple chemical procedure having a high separation efficiency (>99%) was developed and monitored during each foil processing, thanks to the tracer isotopes 61Cu and 66Ga. Nuclear cross sections were measured in the energy range 35–70 MeV by using reference reactions recommended by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to monitor beam flux. In comparison with literature data a general good agreement on the trend of the nuclear reactions was noted, especially with latest measurements, but slightly lower values were obtained in case of 67Cu. Experimental results of the 68Zn(p,2p)67Cu, 68Zn(p,2n)67Ga and 68Zn(p,3n)66Ga reactions were also compared with the theoretical values estimated by using the software TALYS. The production yield of the theranostic radionuclide 67Cu was estimated considering the results obtained in this work.
CU Resin
van Es, E.M., Russell, B.C., Ivanov, P. et al. :"The behaviour of 226Ra in high-volume environmental water samples on TK100 resin"
J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2017) 312: 105, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5203-4
Abstract:
Accurate, low-level measurement of 226Ra in high volume water samples requires rapid pre-concentration and robust separation techniques prior to measurement in order to comply with discharge limits and drinking water regulations. This study characterises the behaviour of 226Ra and interfering elements on recently developed TK100 (Triskem International) extraction chromatography resin. Distribution coefficients over a range of acid concentrations are given, along with an optimised procedure that shows rapid pre-concentration and separation of 226Ra on TK100 resin is achievable for high volume (1 L) water samples without the need for sample pre-treatment.
TK100 Resin
Graves, S.A.: "Evaluation of a chloride-based 89Zr isolation strategy using a tributyl phosphate (TBP)-functionalized extraction resin"
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, Volumes 64–65, September–October 2018, Pages 1-7, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2018.06.003
Abstract:
Introduction
The remarkable stability of the 89Zr-DOTA complex has been shown in recent literature. The formation of this complex appears to require 89Zr-chloride as the complexation precursor rather than the more conventional 89Zr-oxalate. In this work we present a method for the direct isolation of 89Zr-chloride from irradiated natY foils.
Methods
89Zr, 88Zr, and 88Y were prepared by 16 MeV proton irradiation of natY foils and used for batch-extraction based equilibrium coefficient measurements for TBP and UTEVA resin. Radionuclidically pure 89Zr was prepared by 14 MeV proton-irradiation of natY foils. These foils were dissolved in concentrated HCl, trapped on columns of TBP or UTEVA resin, and 89Zr-chloride was eluted in
Results
Equilibrium coefficients for Y and Zr were similar between UTEVA and TBP resins across all HCl concentrations. Kd values of <10−1 mL/g were observed for Y across all HCl concentrations. Kd values of >103 mL/g were observed at HCl concentrations >9 M for Zr, falling to Kd values of
Conclusion
TBP-functionalized resin appears promising for the direct isolation of 89Zr-chloride from irradiated natY targets. Excellent 89Zr recovery efficiencies were obtained, and chemical purity was sufficient for proof-of-concept chelation studies.
TBP Resin
Brügmann et al. "Silver isotope analysis of gold nuggets: An appraisal of instrumental isotope fractionation effects and potential for high-resolution tracing of placer gold"
Chemical Geology, Volume 516, 30 June 2019, Pages 59-67, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.03.015
Abstract:
We describe a technique for high-precision analysis of 109Ag/107Ag ratios in natural and archaeological gold (1.0–120 mg/g Ag) with particular emphasis on the control of Ag yield and effects of instrumental mass bias. After dissolution of mg-sized gold samples in aqua regia and conversion to chlorides, a miniature column filled with the anion exchange resin AG@1-X8 was used for removal of Au from the sample solutions. In a second miniature column made of the Triskem TBP resin Ag was converted from the chloride to the nitrate form. Isotopic analyses on the MC-ICP-MS employed the combination of Pd-doping and standard bracketing and considering the measurements of replicate dissolutions and chromatographic separations for SRM978a and CEZAg reference solutions, the combined analytical uncertainty (2 s) of the analytical method is better than 0.016‰. A solution prepared from several gold nuggets was characterised isotopically (CEZAg with δ109Ag = 0.043 ± 0.015‰) for use as a silver-in‑gold reference material in Ag isotope studies of natural and processed gold.
Results for gold nuggets from three continents indicate a wide variation in Ag concentrations (5 to 123 mg/g) and this is matched by an equally wide range in isotopic compositions (δ109Ag −0.58 to +0.83‰). This is larger than the variation found so far in in native gold from primary deposits (−0.42 to +0.5‰). Although small isotopic effects to lower δ109Ag during strong Ag loss are possible within a single grain, most analysed nuggets are internally isotopically homogeneous. This suggests preservation of the primary δ109Ag in the supergene environment and that gold was sourced from several distinct gold deposits in the catchment. Recent studies, however, indicate that even single primary deposits may be isotopically heterogeneous implying that Ag isotope fractionation is caused by numerous deposition-dissolution cycles in hydrothermal systems. Fine-grained detrital gold from three placers along the Rhine river in Germany show only small differences in δ109Ag (−0.005 ± 0.047 to +0.124 ± 0.007‰, despite being distributed along 480 km of river length. This may indicate thorough mixing of gold grain populations during transport.
The small sample size required for Ag isotope work on gold opens the way for detailed micro-sampling approaches. These may be used to further examine the potential for within-grain isotopic variability related to fluviatile processing and can be used to correlate the composition of the placers with that of grains from primary sources.
TBP Resin
Süfke, F., Lippold, J., Happel, S.: "Improved Separation of Pa from Th and U in Marine Sediments with TK400 Resin"
Anal. Chem., 2018, 90 (2), pp 1395–1401; DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04723
Abstract:
Protactinium-231 is a radionuclide of broad interest in paleoceanography and paleoclimatology. This study describes an improved method for the purification and separation of Pa from marine sediment samples using the new TK400 resin by TrisKem International. The focus lies on the improvement of the separation of the abundant 232Th from the Pa fraction of the sample, which would reduce the peak tailing from 232Th on masses 231 and 233 during ICP-MS measurement. Furthermore, the reusability of TK400 has been tested. For this purpose, the conventional method using Dowex AG1X8 for the separation and purification of Pa has been compared to methods using the TK400 resin. A combination of a Dowex AG1X8 prior to a TK400 column has shown most convincing results. Based on our results we suggest a new efficient procedural method of analyzing 231Pa from marine sediment samples using TK400. Chemical Pa yields for a Dowex-TK400 combination are highest compared to the Dowex only method. Furthermore, the 232Th/231Pa ratio of the Pa-fractions has been reduced by 1 order of magnitude compared to conventional methods with Dowex AG1X8. Additionally, the reusability of TK400 resin up to nine times has been proven. The usage of TK400 is only limited in the presence of samples with a high matrix load (e.g., Fe). Therefore, matrix from sediment samples needs to be removed (here using Dowex resin) before samples are loaded onto TK400. We also report a series of concentration measurements from standard reference materials (UREM-11, NIST 2702), which have been used for 233Pa calibration.
TK400 Resin
Carolina Hernández González, Inmaculada Sierra Bercedo:"Rapid procedure for actinides and 90Sr analysis in emergency urine spot samples applied in the GHSI-RNWG emergency intercomparison exercise"
Appl. Radiat. Isot., in press, available online 17.11.18, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2018.11.007
Abstract:
A rapid radiochemical separation method for quantification of 90Sr, plutonium, americium, curium, uranium and thorium isotopes in urine spot samples has been developed. The validation and suitability of the method has been tested in the emergency intercomparison exercise organised by the Global Health Security Initiative / Radio-Nuclear Threats Working Group. Excellent results were obtained with bias of -0.07 (239Pu) and -0.11 (90Sr). CIEMAT Laboratory also fulfilled the established reporting schedule and submitted the results within 72 hours, as required.
TEVA, TRU and Sr-Resin
Maoyi Luo et al.: "Sequential analyses of actinides in large-size soil and sediment samples with total sample dissolution"
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, Volume 187, July 2018, Pages 73-80, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2018.01.028
Abstract:
There is a growing demand for the determination of actinides in soil and sediment samples for environmental monitoring and tracing, radiological protection, and nuclear forensic reasons. A total sample dissolution method based on lithium metaborate fusion, followed by sequential column chromatography separation, was developed for simultaneous determination of Pu, Am and Cm isotopes in large-size environmental samples by alpha spectrometry and mass spectrometric techniques. The overall recoveries of both Pu and Am for the entire procedure were higher than 70% for large-size soil samples. The method was validated using 20 g of soil samples spiked with known amounts of 239Pu and 241Am as well as the certified reference materials IAEA-384 (Fangataufa Lagoon sediment) and IAEA-385 (Irish Sea sediment). All the measured results agreed very well with the expected values.
TEVA Resin and DGA, N Resin
Wang, Z., Lin, J., Li, S. et al. "Rapid method for accurate determination of actinides (U, Th, Pu and Am) in water samples for emergency response"
J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2018) 315: 103, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5640-0
Abstract:
To rapidly assess the contamination of actinides in emergency water, a method was developed to simultaneously analyze U, Th, Pu and Am. The method consists of two steps: extraction chromatographic separation using UTEVA and DGA resins and isotopic determination of actinides by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICPMS). The whole analytical procedure takes only 8 h and high chemical recoveries of actinides were obtained. The cross spectral interferences between actinides in ICPMS measurement were sufficiently removed. The accuracy was validated by analyzing IAEA-443 seawater sample. The low limits of detection of actinides allow this method to distinguish low level contamination.
UTEVA Resin and DGA resin
Marstren, T. et al. "Chromatographic separation of the theranostic radionuclide 111Ag from a proton irradiated thorium matrix"
Analytica Chimica Acta, Volume 998, 15 January 2018, Pages 75-82, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.10.020
Abstract:
Column chromatographic methods have been developed to separate no-carrier-added 111Ag from proton irradiated thorium targets and associated fission products as an ancillary process to an existing 225Ac separation design. Herein we report the separation of 111Ag both prior and subsequent to 225Ac recovery using CL resin, a solvent impregnated resin (SIR) that carries an organic solution of alkyl phosphine sulfides (R3P = S) and alkyl phosphine oxides (R3P = O). The recovery yield of 111Ag was 93 ± 9% with a radiochemical purity of 99.9% (prior) and 87 ± 9% with a radiochemical purity of 99.9% (subsequent to) 225Ac recovery. Both processes were successfully performed with insignificant impacts on 225Ac yields or quality. Measured equilibrium distribution coefficients for silver and ruthenium (a residual contaminant) on CL resin in hydrochloric and nitric acid media are reported, to the best of our knowledge, for the first time. Additionally, measured cross sections for the production of 111Ag and 110mAg for the 232Th(p,f)110m,111Ag reactions are reported within.
CL Resin
Alves, V.H. et al.: "Automated Purification of Radiometals Produced by Liquid Targets"
Instruments 2018, 2(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/instruments2030017
Abstract:
An automated process for the production and purification of radiometals produced by irradiating liquid targets in a medical cyclotron, using a commercially available module, has been developed. The method is suitable for the production and purification of radiometals such as 68Ga, 64Cu and 61Cu through irradiation of liquid targets and is important for producing high specific activity radioisotopes with a substantial reduction in processing time and cost when compared with the solid target approach. The “liquid target” process also eliminates the need for pre- and post-irradiation target preparation and simplifies the transfer of irradiated material from target to hotcell. A 68GaCl3 solution can be obtained in about 35 min with an average yield of 73.9 ± 6.7% in less than 10 mL of volume. 64CuCl2 solutions can be obtained with an average yield of 81.2 ± 7.8% in about 1 h of processing time. A dedicated single-use disposable kit is used on a commercial IBA Synthera® extension module.
CU Resin
Morrison, S.S., Morrison, E.C., Uhnak, N.E. et al.: "Isolation of Au and Pt radionuclides from deuteron-irradiated platinum using TBP resin"
J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6382-3
Abstract:
A separation procedure was developed and implemented for the isolation of gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) radionuclides from deuteron irradiated Pt using tri-butyl phosphate (TBP) resin. Computational modeling and experimental results of the Au and Pt radionuclide production were reported and compared to literature values. Results of the separation procedure demonstrated a Pt recovery of 98 ± 2% and a Au recovery of 92 ± 7%, in their respective fractions (n = 4 ± 1σ) The decontamination factors were 2900 ± 500 for Au removal from the Pt fraction and 830 ± 30 for Pt removal from the Au fraction (n = 4 ± 1σ).
TBP Resin
Naperstkow, Z., Moore, K., Szames, D. et al.: "Production and standardization of an on-demand protactinium-233 tracer"
J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2018) 318: 703, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6068-x
Abstract:
Protactinium-233 (233Pa) was generated by neutron activation of thorium and isolated by column chromatography using an octanol-impregnated resin. Absolute activity standardization was performed on 233Pa using three independent methods, the results of which agreed within their associated uncertainties. The standardized 233Pa was used to calibrate a secondary standard ionization chamber and high purity germanium detectors to enable a rapid and traceable method for the production and quantification of this radiotracer.
TK400
Jerome, S.M. et al. "Isolation and purification of protactinium-231"
Appl Radiat Isot. 20:18 Apr;134:18-22, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.07.051
Abstract:
Protactinium-231 is one of the lesser known actinides, yet the measurement of this radionuclide is central to dating studies in both paleoclimate and nuclear forensics measurements; furthermore, it is important as the immediate parent nuclide of the 227Ac decay chain. In this paper, we present the preparatory work for an upcoming CCRI(II) supplementary comparison of this radionuclide. The material used in this work was of poorly known provenance, and it was necessary to carry out a chemical purification of this material prior to use. A new extraction chromatography resin, TK 400, which has been developed for the separation of 231Pa, was tested at NPL. The aims of the work were achieved; the recovery of 231Pa was ~85%, the decay products were recovered in good yield (~95%) and stable element impurities were removed.
TK400
Pupillo, G. et al. "New production cross sections for the theranostic radionuclide 67Cu"
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 15, 2018, 41-47, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2017.10.022
Abstract:
The cross sections of the 68Zn(p,2p)67Cu, 68Zn(p,2n)67Ga and 68Zn(p,3n)66Ga reactions were measured at the ARRONAX facility by using the 70 MeV cyclotron, with particular attention to the production of the theranostic radionuclide 67Cu. Enriched 68Zn material was electroplated on silver backing and exposed to a low-intensity proton beam by using the stacked-foils target method. Since 67Cu and 67Ga radionuclides have similar half-lives and same γ-lines (they both decay to 67Zn), a radiochemical process aimed at Cu/Ga separation was mandatory to avoid interferences in γ-spectrometry measurements. A simple chemical procedure having a high separation efficiency (>99%) was developed and monitored during each foil processing, thanks to the tracer isotopes 61Cu and 66Ga. Nuclear cross sections were measured in the energy range 35–70 MeV by using reference reactions recommended by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to monitor beam flux. In comparison with literature data a general good agreement on the trend of the nuclear reactions was noted, especially with latest measurements, but slightly lower values were obtained in case of 67Cu. Experimental results of the 68Zn(p,2p)67Cu, 68Zn(p,2n)67Ga and 68Zn(p,3n)66Ga reactions were also compared with the theoretical values estimated by using the software TALYS. The production yield of the theranostic radionuclide 67Cu was estimated considering the results obtained in this work.
CU Resin




